Don’t have an account?
Select the donation type you’d like to make
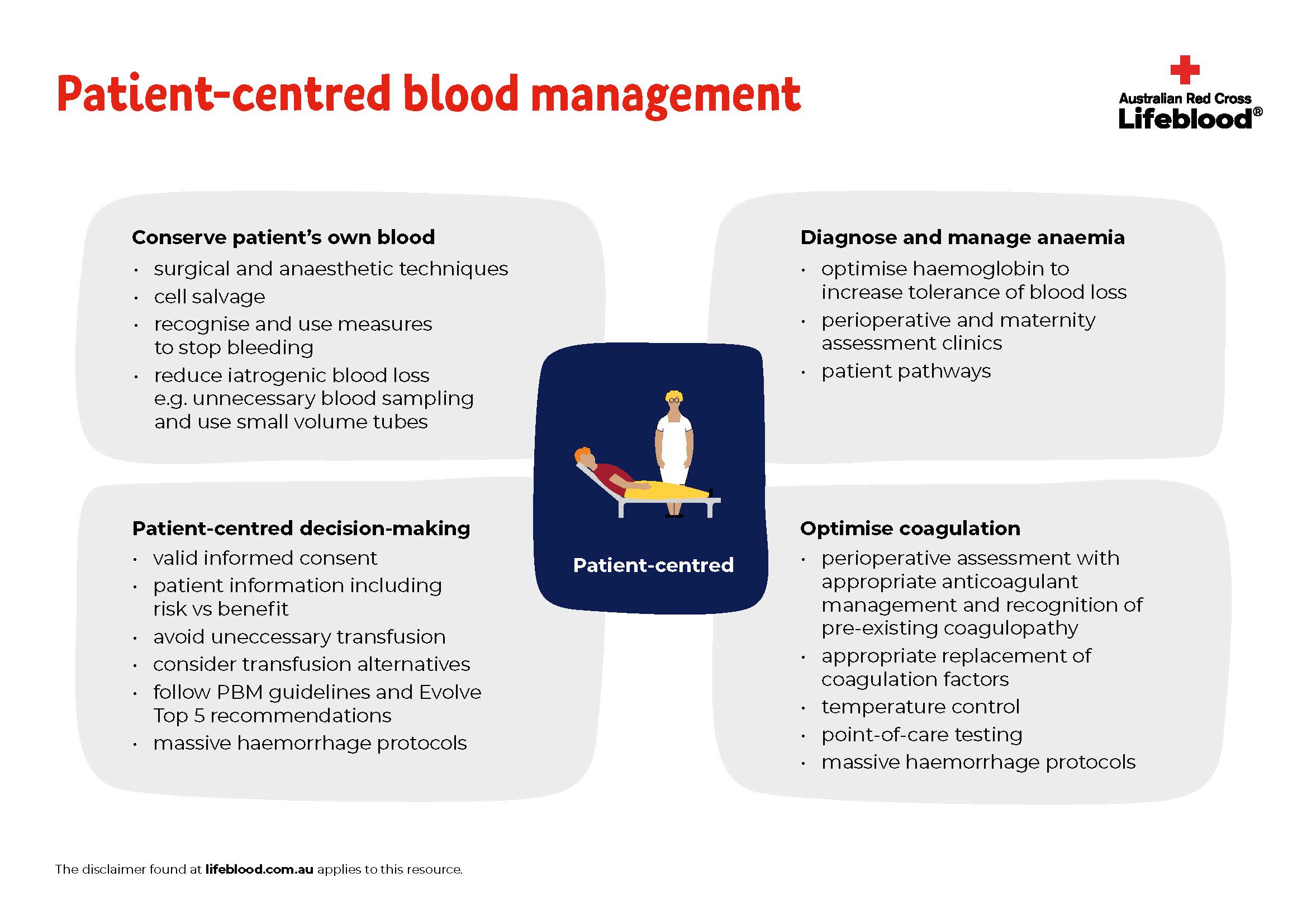
"Patient blood management (PBM) is a patient-centred, systematic, evidence-based approach to improve patient outcomes by managing and preserving the patient's own blood, while promoting patient safety and empowerment."
This definition is from the International Anesthesia Research Society article: A Global Definition of Patient Blood Management.
The three pillars of PBM that underpin practice are:
- optimising the patient's own blood, such as identifying and optimising anaemia and iron deficiency
- minimising blood loss, such as surgical techniques and therapies that reduce blood loss and use of cell salvage, and
- optimising the patient's tolerance of anaemia.
Updated April 2025
Further information
Related topics
Online learning

