ABO blood group antigens and antibodies
ABO is the most important of all the blood group systems.
There are four main blood groups in the ABO blood group system, determined by whether an individual's red cells carry the A antigen, the B antigen, both A and B antigens, or neither antigen.
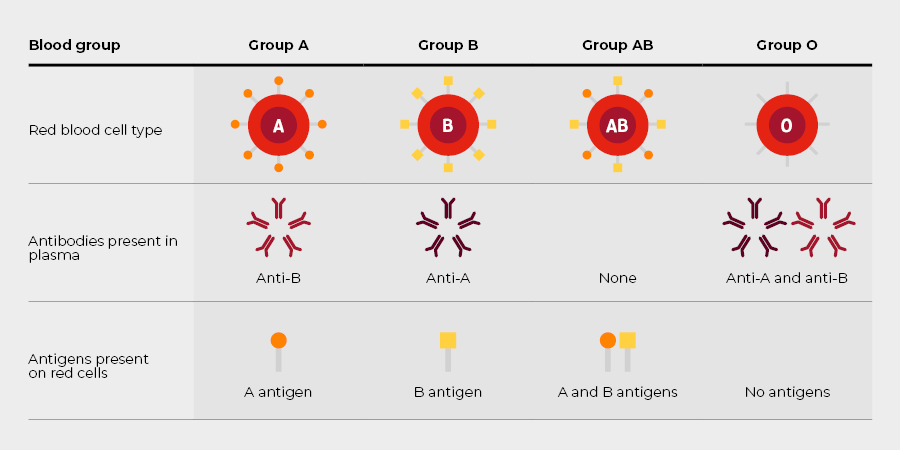
From early childhood, normal healthy individuals have naturally occurring red cell antibodies against the A and/or B antigens that are not expressed on their own cells. These antibodies are also known as isohaemagglutinins.
ABO antibodies are mainly IgM immunoglobulins but can also be IgG. Anti-A reacts with red cells of group A or AB, and anti-B with red cells of group B or AB. The antibodies bind to transfused red cells carrying the corresponding antigen and trigger an immune response, causing the red cells to haemolyse. For example, if group A red cells are transfused into a group O recipient, the recipient’s anti-A binds to the transfused red cells.
If ABO incompatible red cells are transfused, immediate red cell haemolysis can occur. An ABO incompatible transfusion reaction is an acute haemolytic transfusion reaction. This reaction, which may be fatal, can lead to overwhelming complement activation and result in shock, renal failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
If an ABO incompatible transfusion reaction is suspected, the transfusion should be stopped immediately.
ABO genes
Blood groups are inherited from our parents similarly to other genetic traits (e.g. eye colour).
The ABO blood group system is determined by the ABO gene, which is found on chromosome 9. The four ABO blood groups, A, B, AB and O, arise from inheriting one or more of the alternative forms (or alleles) of this gene namely A, B or O.
Genetic combinations of ABO blood groups
| Blood group | Possible genes |
|---|---|
| A | A/A or A/O |
| B | B/B or B/O |
| AB | A/B |
| O | O/O |
The A and B alleles are dominant over O alleles and so A and B antigens will be expressed on the red cells whenever an A or B allele is present along with O allele.
The A and B alleles are also considered codominant, meaning both A and B antigens will be expressed when the alleles are inherited together. O alleles do not produce either A or B antigens and are sometimes called ‘silent' alleles.
ABO inheritance patterns
Below are the possible blood groups that children may inherit according to the combination of parental blood groups.
| Parental blood groups | Child's blood group |
|---|---|
| O and O | O |
| O and A | O or A |
| O and B | O or B |
| O and AB | A or B |
| A and A | A or O |
| A and B | O or A or B or AB |
| A and AB | A or B or AB |
| B and B | O or B |
| B and AB | B or A or AB |
| AB and AB | A or B or AB |
Updated March 2025