Use of fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
Indications
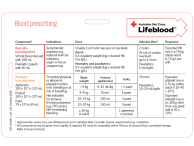
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is used for patients with one or more coagulation factor deficiencies who are bleeding or at risk of bleeding, and where a specific alternative therapy or factor concentrate is unavailable.
FFP may be indicated to replace labile plasma coagulation factors during
- major haemorrhage requiring massive transfusion,
- cardiac bypass for the treatment of bleeding,
- bleeding in patients with decompensated liver disease or
- bleeding in patients with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation
- undergoing an invasive procedure with coagulopathy
Plasma exchange with FFP is an accepted treatment for patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP).
Refer to the National Blood Authority’s Patient Blood Management Guidelines and other evidence-based clinical guidelines for specific guidance to support clinical decisions about appropriate transfusion practices and the use of blood components.
Our Prescribing fresh frozen plasma resource provides guidance for FFP transfusion based on the above guidelines.
When is FFP not indicated?
Do not use FFP in the following circumstances:
- when you can correct coagulopathy effectively with specific therapy, such as vitamin K, cryoprecipitate, factor VIII or other specific factor concentrates,
- in plasma exchange procedures except for treatment in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP),
- treatment of immunodeficiency states,
- when 4-factor Beriplex® is used in life-threatening warfarin-related bleeding,
- in non-bleeding patients with abnormal coagulation tests,
- prior to procedure when the INR is only mildly elevated (INR < 1.8),
- in patients with liver disease who are not bleeding or undergoing invasive procedure.
Dosage
In most cases, the dose will be 15 mL/kg. Consider:
- 10-15 mL/kg for standard adult dose,
- higher dosing may be required in massive haemorrhage and should be guided by coagulation testing,
- 10-20 mL/kg for paediatric patients < 30 kg.
Updated May 2025